BE A MEDICAL LEADER IN PRECISION MEDICINE
In 2000 when the Human Genome was the frist time accessable by the winnings of Craig Venter with Celera and the Human Genome Project our medicine is in transformation visible in the digitalisation and molecularistaion of medicine.
150 years from Virchow to Venter:
150 years ago Virchow started the Cellular Pathology at Charité in Berlin:
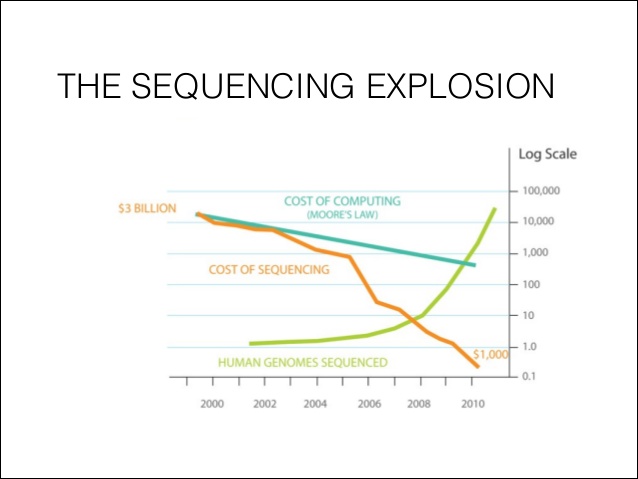
Since 2000 we are in the transformation of Cellular towards Molecular Pathology towards Precision Medicine by the Key-Technology of Next-Generation-Sequencing with falling sequencing-coasts under 1.000 $ for one whole genome today – though NGS-Seq will be part of your daily diagnostic routine:
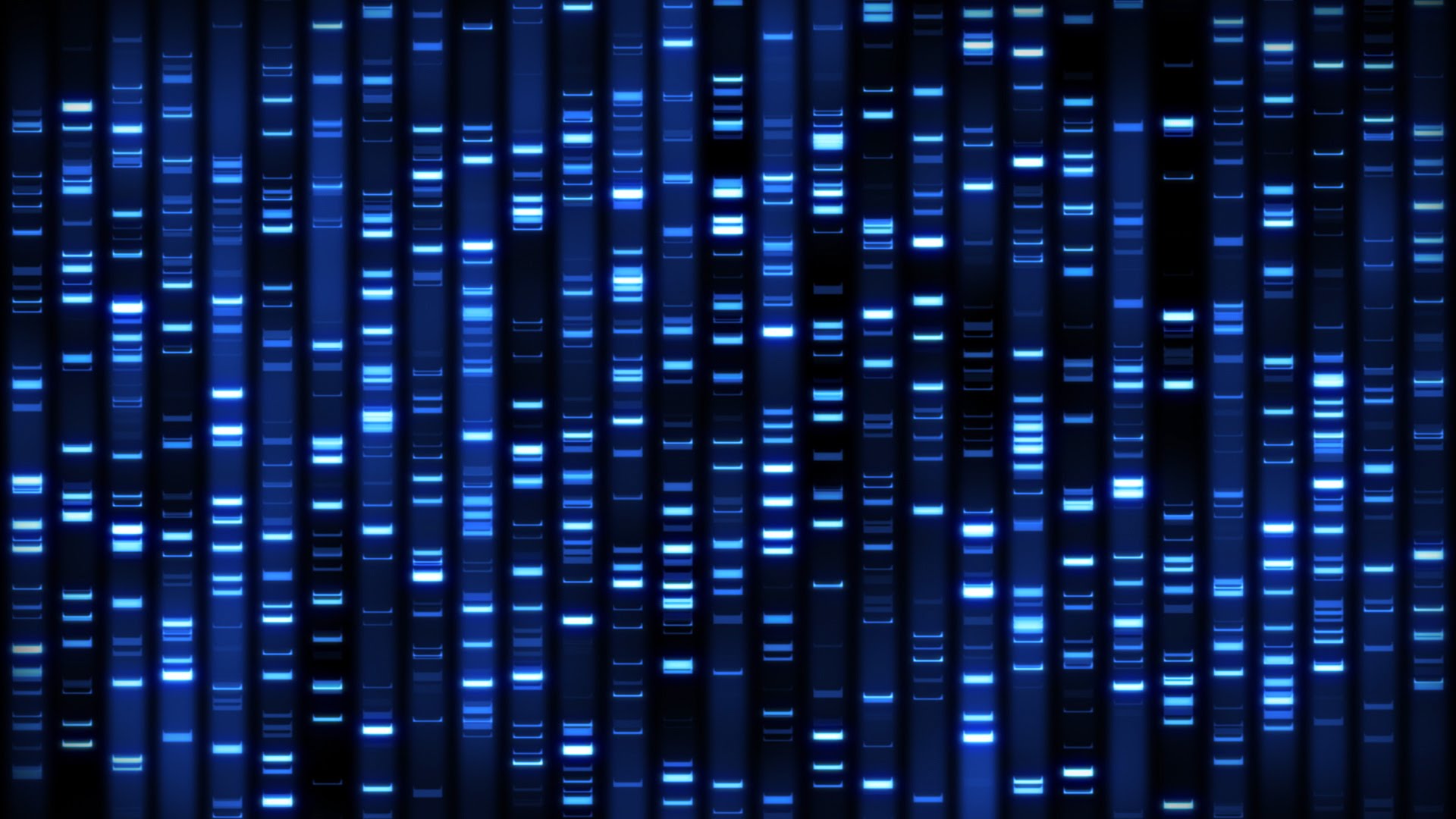
 Next-Generation-Sequencing as a basis for molecular medicine.
Next-Generation-Sequencing as a basis for molecular medicine.
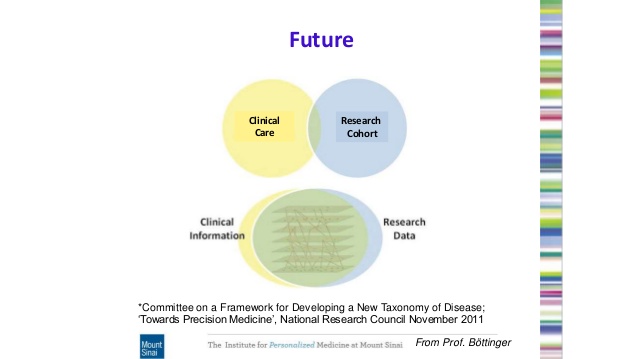
What is Precision Medicine?
Right now, most medical treatments are designed for the average patient – called the traditional „one-fits-many“ concept of the pharmaceutical industry. Precision medicine, on the other hand, matches each patient with the treatment that will work best for them by the knowledge of their disease on the molecular level and all the traditional levels of medicine as cellular pathology, CT-, MRI- and PET-Imaging, traditional Laboratory and all his Data in his Electronic Medical Record.
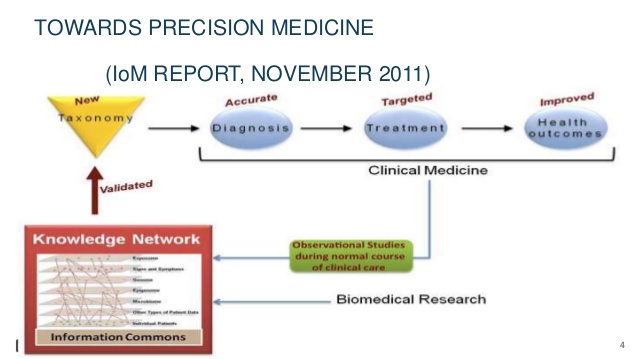
Today like in Google Maps every patient needs to be for an accurate diagnosis digitized in several molecular levels (genomics, transcriptomics, epigenomics, mircobiomics, exposome). For most molecular diseases (Cancer, Immunologic & Inflamatory and Metabolic Diseases) the analysis of their Genome and Transcriptome will give enough deep insight to find the right indivdual pharmagenomic treatment towards better outcome and surviving for the patients. Precision Medicine takes individual variation into account: variation in our genes, environment, lifestyle, and even in the microscopic organisms that are living inside of us.
“The best chance of favorable outcome is getting the initial therapy after molecular individual diagnosis right.”: PRECISION MEDICINE FIRST.
Molecular Medicine at the genomic age:
The Genomic Revolution in Medicine: In 2001, a human genome cost about $100 million to sequence. 2014 began with an announcement of a new machine that could sequence 16 human genomes in 3 days at a cost of about $1,000 per genome. What this means for patients is that whole-genome sequencing is now as affordable as many routine medical tests, and it’s becoming increasingly available. For no more than the cost of an MRI scan, patients will be able to obtain their entire genomic sequence, a resource that will continue to inform medical decisions for them over the course of their lifetime.
Sequencing even one human genome generates a lot of information—about 200 gigabytes of raw data-and it takes some serious computational power to chug through it. With a deluge of new sequence data hitting the networks each day, efforts have turned to developing tools and systems for storing, sharing, and analyzing this data on a large scale. With these tools, researchers can analyze genomic information from large numbers of people – some with disease and others without. It may seem counterintuitive, but the more genomic information your doctors understand about everybody else, the better equipped they are to offer individualized care to you. Though care for you and your loved one`s by asking your MD for Precision Medicine and Precision Prevention.
Beyond the genome
Understanding how genetic variations contribute to health is just one aspect of precision medicine. While the genome is set for life, the expression of our genes fluctuates over time and in response to the environment. Additional approaches to precision medicine involve measuring levels of proteins, RNAs, or metabolic products. Along with genomics, proteomics, epigenomics, and metabolomics can help inform medical choices for individual patients.
The field also incorporates what we are learning about the microbes that live in and on our bodies and how they can be manipulated to influence health and disease. It combines the latest in stem cell science with 3D printing technology to build replacement skin, blood vessels, and bones. It includes techniques for engineering a patient’s own immune cells to attack cancer and other diseases, and computer algorithms for building customized diets for diabetic patients.
Beyond treating disease, precision medicine includes approaches to diagnostics, prevention, and screening:
- Methods for identifying those who are at risk before disease strikes;
- Analytical tools for predicting which prevention strategies will work best for which patients;
- Screening methods that can identify early signs of disease before symptoms emerge;
- Diagnostic methods for identifying subtypes of disease that may look the same on the surface but respond very differently to treatment;
- Tests that can identify disease carrier status for prospective parents;
- Devices for managing diseases and for tracking and guiding recovery
Be part of the Precision Medicine value-chain:
Precision Medicine: The Patients-Focus
As a medical doctor you should be as well informed as your empowered patients with their access to online informations with their 8 billion smartphones – even you should be at the frontline of precision medicine to navigate your patient.
Medicine will be a transparent online real-time-medicine in which population profiles can be used for diagnosis and therapy. These data and profiles will have to be controlled by all stakeholders in the health system for patient data saftey, but there will also be a parallel health world where the younger technique afine generation shares their health data for the benefit of all.
Be be a driving force in this transformation. Be a Leader in Precision Medicine.
Today all banking is digital – tomorrow all medicine will be molecular & digital:
Data privacy and protection will be guaranteed by all stakeholders in all health systems like we are acting globally in digital banking in a data saftey world.
Let`s save the lives of patients together.